1. What is Mary-Morstan ?
Mary-Morstan is a multi objective modular framework to automatically configure machine learning algorithms. This python automated machine learning tool is based on evolutionary algorithms.
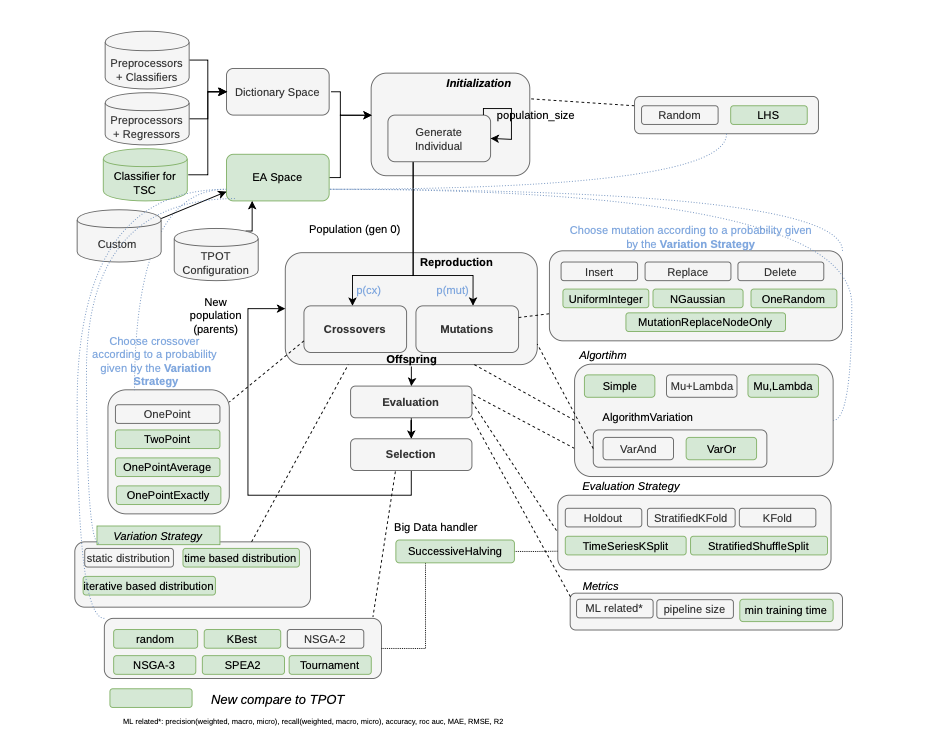
Mary-Morstan is modular in such a way that the exploration versus exploitation process can be tuned through the specification of an Evolutionary Algorithm (EA) space. It also allows to deal with big data files and various of classification and regression problems. Mary-Morstan starts with a phase of initialization, which includes three parts.
-
The selection of a Machine Learning space, containing all the algorithms and their associated parameters. This dictionary space is very common in other AutoML solutions.
-
The selection of an EA space, specifying and configuring all the different EAs components. To the best of our knowledge, there is no such a feature in the current AutoML solutions.
-
The generation of initial ML pipelines.
Passed the initialization phase, the framework starts an EA loop process where the ML pipelines are subject to variations, evaluations and selection until a budget is exhausted. The budget can be implemented in different manners. Usually it is represented as a fixed number of iterations (generations). An alternative to the budget can be an amount of time, or when there is no more progress (convergence).
-
Architecture of Mary-Morstan (see Laurent Parmentier’thesis):
| To try this AutoML framework, go here |
2. Installation
3. Using Mary Morstan
First, you need to activate the virtual environment created during the installation phase:
. venv/bin/activateTwo methods are possible. The first one uses the supplied python API, while the second uses the executable bin/mary-morstan
3.1. First method: programming in Python
Here is a classical basic usage:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection._validation import _score
import numpy as np
import importlib
import logging
from marymorstan.marymorstan import MaryMorstan
log_level = getattr(logging, 'ERROR')
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s [%(filename)s:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s', level=log_level)
dataset_preprocessing_module = importlib.import_module("datasets.iris_dataset_preprocessing") (1)
dataset = dataset_preprocessing_module.MyDataSetPreprocessing("iris")
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(dataset.get_X(), dataset.get_y(), test_size=.25, random_state=42)
mm = MaryMorstan(generations=4, population_size=5, random_state=np.random.RandomState(42)) (2)
pipelines = mm.optimize(X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train,
random_state=np.random.RandomState(42)) (3)
best_pipeline = MaryMorstan.best(pipelines) (4)
# then you can save it as a string and easily reimport later
best_pipeline_str = str(best_pipeline)
print("best pipeline found:", str(best_pipeline))
print("Objectives:", str(mm.objectives))
print("resulting scores") (5)
print(f'current validation_scores: {str(list(best_pipeline.fitness.weighted_values))}')
best_pipeline_compiled = best_pipeline.compile()
best_pipeline_compiled.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_scores = _score(best_pipeline_compiled, X_train, y_train, mm.objectives.scorers).values()
test_scores = _score(best_pipeline_compiled, X_test, y_test, mm.objectives.scorers).values()
print("train scores :", str(list(train_scores)))
print("test scores :", str(list(test_scores)))| 1 | use the dataset framework to download a dataset |
| 2 | initialisation of marymorstan with various parameters |
| 3 | run the process |
| 4 | get best found pipeline |
| 5 | display result scores |
Execute this python script :
python3 ./misc/simpleDemo.py3.2. Second method: the mary-morstan executable
bin/mary-morstan is a command line tool. You pass it various parameters. Some of these are dedicated to the dataset and the way it is pre-processed. Various datas resulting from the process are then displayed on the console.
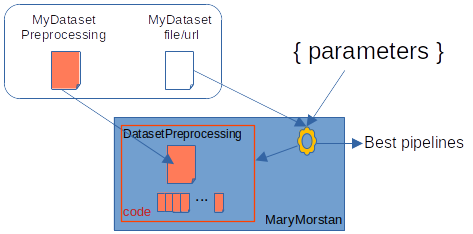
Here is the script equivalent to the previous method
#!/bin/bash
mary-morstan --dataset 'iris' --dataset-preprocessing "datasets.iris_dataset_preprocessing" \
--generations 4 --population-size 5 --seed 42 --test-size-ratio .25 \
--log-level=ERROR \
--print-best-pipeline-only --test-best-pipelineExecute this bash script :
sh ./misc/simpleDemo.sh3.2.1. mary-morstan parameters on the command-line
mary-morstan offers several arguments that can be provided at the command line. To see a brief overview, enter the following command:
mary-morstan --helpThe table below provides a full description of these arguments. Most of these arguments are optional. In the absence of an argument, a default value is used.
Argument |
valid value(s) |
default value |
Description |
-h, --help |
None |
None |
display the list of available arguments |
--generations |
integer |
100 |
number of iterations to run the optimization process |
--population-size |
integer |
100 |
number of individuals in the genetic programming optimization process |
--init-pipeline-size-min |
integer |
3 |
min size of the generated pipeline structure |
--init-pipeline-size-max |
integer |
3 |
max size of the generated pipeline structure |
--allow-fit-to-valid-pipeline |
None |
false |
Mechanism similar to TPOT (equivalent to decorator _pre_test) where each pipeline is fitted with a small generated samples in order to be considered as valid. |
--max-number-of-fits |
integer |
5 |
Only works if --allow-fit-to-valid-pipeline is specified" |
--wall-time-in-seconds |
integer |
None |
|
--budget-per-fit-to-valid-pipeline-seconds |
float |
2 |
Only works if --allow-fit-to-valid-pipeline is specified |
--evaluation-strategy |
holdout, k_fold, repeat_k_fold, shuffle_split, stratified_k_fold, stratified_shuffle_split, time_series_k_split |
holdout |
|
--evaluation-summarize-method |
SUMMARIZE_METHOD.MEAN, SUMMARIZE_METHOD.MEDIAN |
SUMMARIZE_METHOD.MEAN |
|
--evaluation-test-size |
float |
.1 |
set the size for evaluation, used by stratified split strategies |
--evaluation-n-splits |
integer |
5 |
number of splits for evaluation, used by stratified split strategies |
--problem-type |
classification_binary, classification_multiclass, regression, timeseries_classification, timeseries_regression |
classification_multiclass |
Important to be specified for Time Series problem, it will disable the shuffle of the dataset |
--objectives |
accuracy, balanced_accuracy, tpot_balanced_accuracy, roc_auc, f1, precision,recall, precision_weighted, precision_macro, precision_micro, recall_weighted,recall_macro, recall_micro, f1_weighted, f1_macro, f1_micro, roc_auc_ovr, roc_auc_ovo, negative_root_mean_square, rmse, mae, r2, min_pipeline_size, min_training_time |
None |
multiple objectives can be set |
--seed |
integer |
None |
|
--dataset |
string |
iris |
the name of the dataset |
--dataset-preprocessing |
string |
datasets .iris_dataset_preprocessing |
the name of the python module which download the dataset |
--dataset-fill-nan |
None |
fill NaN values if specified |
|
--dataset-drop-columns-with-unique-value |
False |
drop column with unique value if specified |
|
--test-size-ratio |
float |
.25 |
|
--enable-statistics |
false |
||
--store-statistics |
string |
statistics.parquet |
Support .json and .parquet (require fastparquet library) |
--log-level |
string |
INFO |
|
--search-space |
string |
None |
set a yaml file which defines the search space (estimators and preprocessors) |
--evolutionary-algorithms-space |
string |
None |
set a yaml file which defines the ea space search |
--evolutionary-algorithms-parameters |
json |
None |
Pass a dictionary with parameters in case you want customize in a different way than through the ea space file. |
--budget-per-candidate-seconds |
float |
300 |
maximum training time for a candidate, if exceeded it is discarded/invalid |
--number-of-jobs |
integer |
1 |
-1 to use all CPUs, 1 to not use parallelism |
--number-of-pipeline-failed-allowed |
integer |
0 |
-1 to disable |
--successive-halving |
boolean |
FALSE |
if set, improve the performance with large datasets |
--successive-halving-minimum-population-size |
float |
1. |
|
--successive-halving-initial-budget |
float |
.1 |
|
--successive-halving-maximum-budget |
float |
1. |
|
--print-best-pipeline-only |
None |
FALSE |
if true, display the best pipeline according to the objectives |
--test-best-pipeline |
NONE |
FALSE |
The best pipeline issued from the optimization will be trained with the whole training set and tested with the whole test set. |
see http://kutt.parmentier.io/tpot-sh for an explanation of the advantages of successive-halving-* parameters
4. Discover Mary Morstan by example
There are many ways to discover Mary-Morstan. There are different scripts that use different configurations and different data sets. In the following directories, you’ll find :
-
datasets contains various python classes to download different (remote) datasets
-
misc different scripts and files for unit-tests and integration-tests (do _make integration_tests)
-
examples jupyter notebooks with various examples
-
tests unit tests (do make unit-tests)
-
benchmarks contains python script for benchmark tests (do _make benchmarks_tests)
5. Citing Mary-Morstan
If you use or reference Mary-Morstan in a scientific publication, please consider citing at least one of the following papers:
Laurent Parmentier. Mary-Morstan : a multi-objective modular framework to automatically configure machine learning algorithms. Data Structures and Algorithms [cs.DS]. Université de Lille, 2022. English. ⟨NNT : 2022ULILB004⟩. ⟨tel-03904161⟩
BibTeX entry:
@phdthesis{parmentier:tel-03904161,
TITLE = {{Mary-Morstan : a multi-objective modular framework to automatically configure machine learning algorithms}},
AUTHOR = {Parmentier, Laurent},
URL = {https://theses.hal.science/tel-03904161},
NUMBER = {2022ULILB004},
SCHOOL = {{Universit{\'e} de Lille}},
YEAR = {2022},
MONTH = Apr,
KEYWORDS = {Machine learning ; Automation ; Evolutionary algorithms ; Compromis exploration-exploitation},
TYPE = {Theses},
PDF = {https://theses.hal.science/tel-03904161/file/These_PARMENTIER_Laurent.pdf},
HAL_ID = {tel-03904161},
HAL_VERSION = {v1},
}The Mary Morstan framework project open source:
BibTeX entry:
@software{mary-morstan,
author = {{Laurent Parmentier, University of Lille - CRIStAL - Orkad Team}},
title = {Mary-Morstan Auto-ML Framework},
url = {https://gitlab.cristal.univ-lille.fr/orkad-public/mary-morstan.git},
version = {0.20},
date = {2024-01-17},
}
----the Mary-Morstan framework also exploits the contributions of these 2 articles:
Laurent Parmentier, Olivier Nicol, Laetitia Jourdan, Marie-Eléonore Kessaci. AutoTSC: Optimization Algorithm to Automatically Solve the Time Series Classification Problem. ICTAI 2021 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Nov 2021, Washington, United States. ⟨hal-03472255⟩
BibTeX entry:
@inproceedings{parmentier:hal-03472255,
TITLE = {{AutoTSC: Optimization Algorithm to Automatically Solve the Time Series Classification Problem}},
AUTHOR = {Parmentier, Laurent and Nicol, Olivier and Jourdan, Laetitia and Kessaci, Marie-El{\'e}onore},
URL = {https://hal.science/hal-03472255},
BOOKTITLE = {{ICTAI 2021 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence}},
ADDRESS = {Washington, United States},
YEAR = {2021},
MONTH = Nov,
HAL_ID = {hal-03472255},
HAL_VERSION = {v1},
}Laurent Parmentier, Olivier Nicol, Marie-Eléonore Kessaci, Laetitia Jourdan. TPOT-SH: a FasterOptimization Algorithm to Solve the AutoML Problem on Large Datasets. ICTAI - International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Nov 2019, Portland, United States. ⟨hal-02430799⟩
BibTeX entry:
@inproceedings{parmentier:hal-02430799,
TITLE = {{TPOT-SH: a FasterOptimization Algorithm to Solve the AutoML Problem on Large Datasets}},
AUTHOR = {Parmentier, Laurent and Nicol, Olivier and Kessaci, Marie-El{\'e}onore and Jourdan, Laetitia},
URL = {https://hal.science/hal-02430799},
BOOKTITLE = {{ICTAI - International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence}},
ADDRESS = {Portland, United States},
YEAR = {2019},
MONTH = Nov,
HAL_ID = {hal-02430799},
HAL_VERSION = {v1},
}